![]()
Ready To Start Hiring?
Successful hiring starts with a simple step
Your leadership style is a cumulation of all behavioral approaches you take to influence, motivate, direct, manage, and support your teammates and employees. It is typically reflective of your personality, experience, and your environment.
However, using an unsuitable leadership style, one inappropriate for the people and situation involved, can leave lasting consequences on the organization and its people.
A study by Daniel Coleman, captured in a Harvard Business Review article, evaluated over 3,000 middle-level managers to find out specific leadership behaviors and their effects on profitability. The results revealed that a manager’s leadership style was responsible for 30% of an organization’s profitability.
This implies that proper identification, understanding and application of appropriate leadership styles at the right time can increase innovation and success, and generate more efficient processes in an organization.
That said, let’s talk about:
In 1939, a group of researchers led by psychologist Kurt Lewin identified different leadership styles—developing Lewin’s Leadership Theory.
Although further research has identified more distinct types of leadership, this early study was significant and established three major leadership styles that function as a framework for more defined leadership styles.
They are:
Also called autocratic leadership. In this leadership style, direction comes from the top—one person who leads a company or team. This person determines all strategies and controls all the decisions, taking little to no input from other group members.
Autocratic leaders are not focused on collaboration with those in their team/organization; they don’t request feedback and bear the sole responsibility for decisions and their outcomes.
This leadership style works best in organizations and teams where the operations require quick decision-making or in small businesses with few employees.
Advantage
Disadvantage
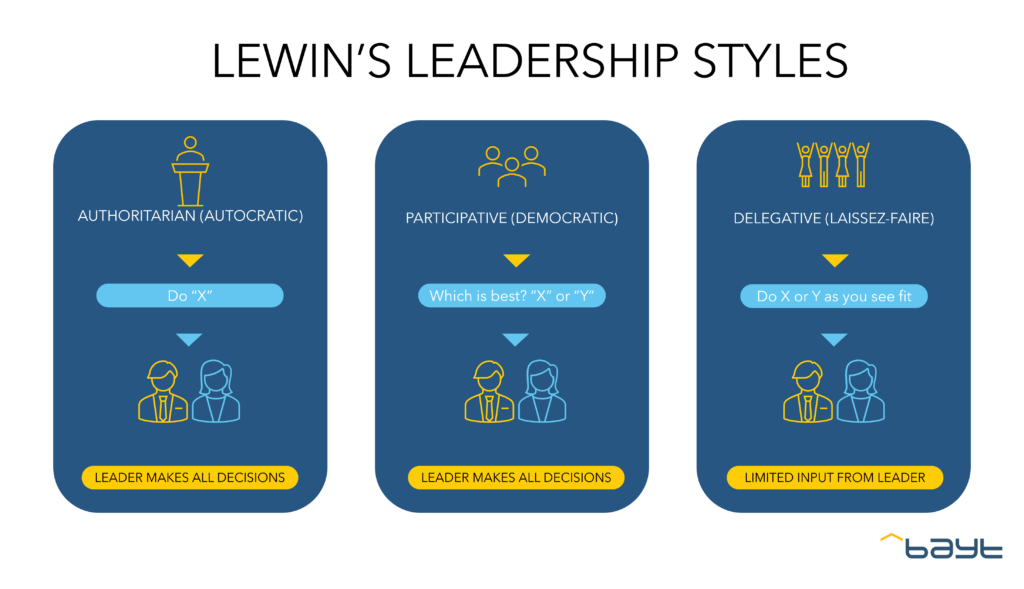
This style of leadership, also called participative leadership, takes into full consideration the employees being led. The manager leads the team by encouraging collaboration between team members, getting input from them and discussing implementation processes with them.
Participative leadership works best in situations where group members are skilled and eager to share their knowledge, thus it falls apart quickly if the leader does not trust their team. So, democratic leaders must have a team of dependable subject-matter experts to guarantee well-executed processes.
Democratic style of leadership works best in organizations when there is enough time to allow people to contribute, develop a plan, then vote on the best course of action.
Advantages
Disadvantage
Let it go, leave it be.
That is the literal translation of the French phrase, laissez-faire. As its interpretation implies, this style of leadership is a hands-off one.
Here, leaders step back and give their team members the necessary tools, resources and information to carry out their tasks. Hence, the employees are free to organize (and disorganize), plan (and unplan), make (or mar) decisions etc.
This leadership style, also known as delegative leadership, is usually more empowering to employees in creative industries like the entertainment industry, advertising industry, research and development and IT. For example, in the entertainment industry, directors may tell actors and crew members to think outside the box and be inventive. Likewise, in IT departments, employees are bound to perform excellently when they can be innovative and inventive.
However, employers who employ this leadership style (or intend to) must be extra careful. According to Kurt Lewin, it is the least satisfying and the least effective. Lewin noted that laissez-faire leadership tended to result in teams being directionless, reckless and where members did not take responsibility.
Advantages
Disadvantages
With the above explanations, you should be able to identify your own natural leadership style and adapt it to fit your workplace conditions. However, if you still have issues doing so, or need confirmation of your style, use this leadership questionnaire to find your style.
![]()
Successful hiring starts with a simple step